If you’re like many managed security services providers (MSSPs), odds are your clients are being overwhelmed by malware and potentially unwanted applications (PUAs) such as spyware and adware. MSSPs have been vigilant about malware and PUAs for years, but 2017 is bringing cause for greater concern. Even though proactive MSSPs continue to boost investment in security technologies, more attacks are succeeding. These and other alarming findings are contained in the June 2017 edition of the Webroot Quarterly Threat Trends report.
In particular, the popularity of ransomware has rapidly increased and it’s causing major operational problems for MSSPs’ clients, as well as damage to the MSSPs’ reputations. As many security professionals know, first-generation antimalware technologies such as signature-based antivirus software are just not effective at detecting and stopping current malware and PUAs on endpoints or networks.
The good news is that sandboxing, endpoint protection suites, and other newer antimalware techniques can deliver much stronger malware and PUA detection capabilities. The bad news? These technologies are resource-intensive because they depend on queueing files for analysis and monitoring each file’s behavior during execution. This can introduce unacceptable latency that disrupts your clients’ business operations.
Webroot Solution: Machine-Learning Based Technology
New advances in machine learning from Webroot have enabled it to develop innovative malware detection capabilities to identify traditional, zero-day, and polymorphic malware—even malware that avoid being detected by sandboxing techniques. Webroot has evolved its own technologies to complement existing malware detection products by addressing their major drawbacks:
- Resource consumption
- Latency
- Dependence on signatures
Webroot created a new patent-pending technology called Webroot BrightCloud® Streaming Malware Detection, which is significantly faster than signature-based and sandboxing techniques, and it’s available for other vendors to integrate into their security solutions. This machine learning-based technology combats the challenges of zero-day, polymorphic, and highly-targeted malware, blocking malicious files in transit at the network edge—without needing to download the entire file—and effectively complements existing antimalware solutions.
Figure 1 below illustrates the basic Streaming Malware Detection architecture:
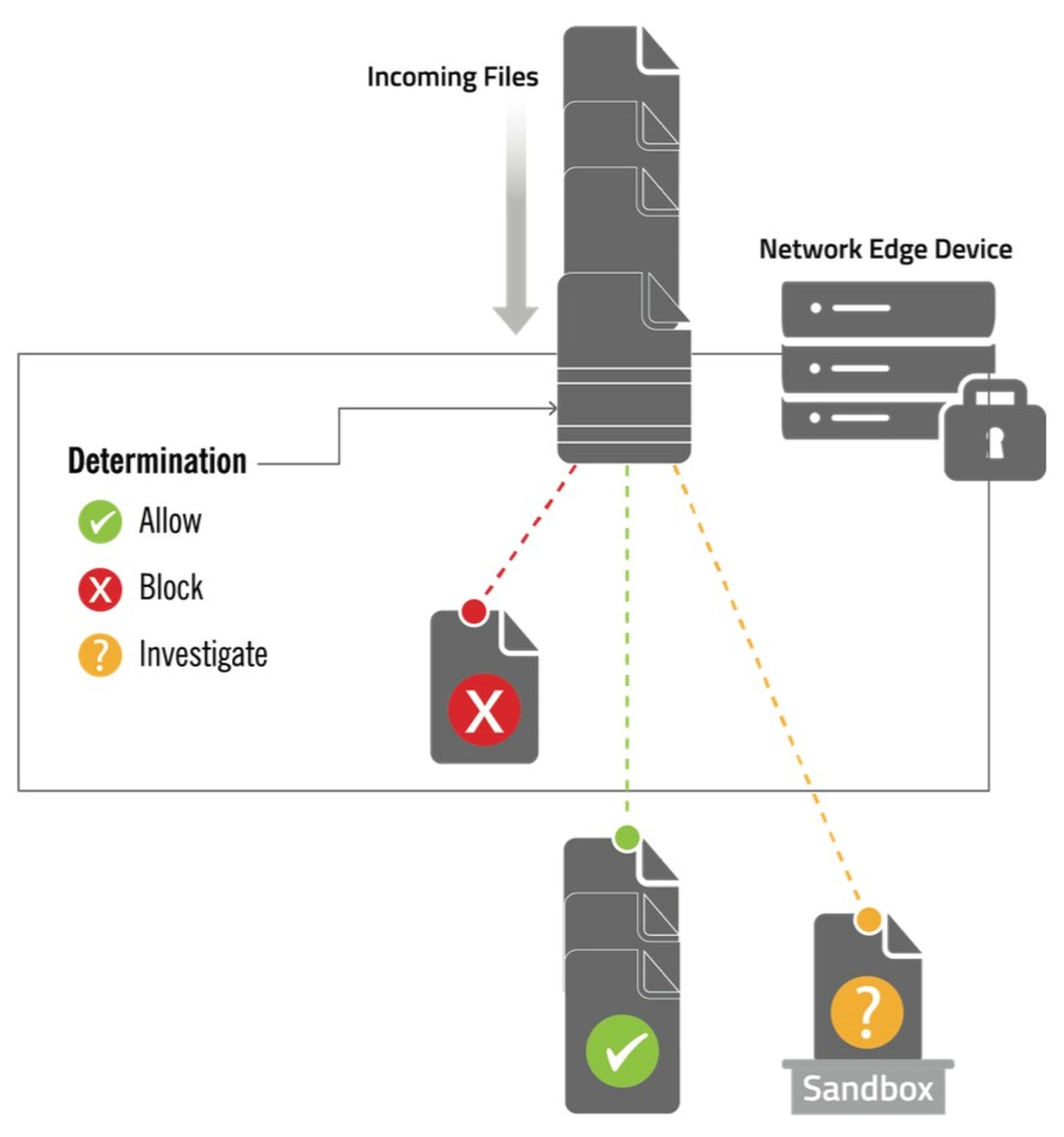
Figure 1: Webroot rapidly identifies just-released malware and PUA files.
Files attempting to reach hosts within your client’s organization enter the Streaming Malware Detection-enabled solution, which is located in a dedicated appliance at the edge of the network. Streaming Malware Detection analyzes each file and chooses one of the following actions:
- Allow: Streaming Malware Detection recognizes the file as known-benign or otherwise determines it poses no threat to the organization. There is no need to send the file to the sandbox for further evaluation, so the solution passes the file on to its destination.
- Block: Streaming Malware Detection has determined that the file is malicious (malware or PUA), so it does not permit it to go any further.
- Investigate: Streaming Malware Detection cannot determine if the file is benign or malicious, so it sends it to the sandbox or other investigative solution for further analysis and decision making.
Through this architecture, Streaming Malware Detection takes a large burden off sandboxing technologies, as well as other security controls like traditional signature-based antivirus software and endpoint protection suites that are also looking for malware and PUAs. This architecture avoids slowing down network traffic by analyzing files as they stream through the network.
The Streaming Malware Detection architecture is also self-contained, enabling determinations to be made locally by the network device. There is no need to constantly access resources in the cloud or elsewhere outside the organization’s networks in order to make determinations.
In essence, Streaming Malware Detection works as a network-based pre-filter that reduces the number of sandboxes, endpoint protection suites, and other tools you’ll need to analyze files. The combination of a sandboxing technology or endpoint protection suite and a Streaming Malware Detection-enabled solution helps improve file delivery times while enabling MSSPs to maximize return on investment for their existing security technologies.
Find Out More
To learn more about the latest malware and PUA trends, as well as complete details on how Webroot BrightCloud® Streaming Malware Detection functions, download your free copy of the June 2017 Webroot Quarterly Threat Trends report.
Questions? Simply fill out the online Request for Contact form and you’ll receive a call from a Webroot Technology Expert.
Guest blog courtesy of Webroot. Read more Webroot guest blogs here.




